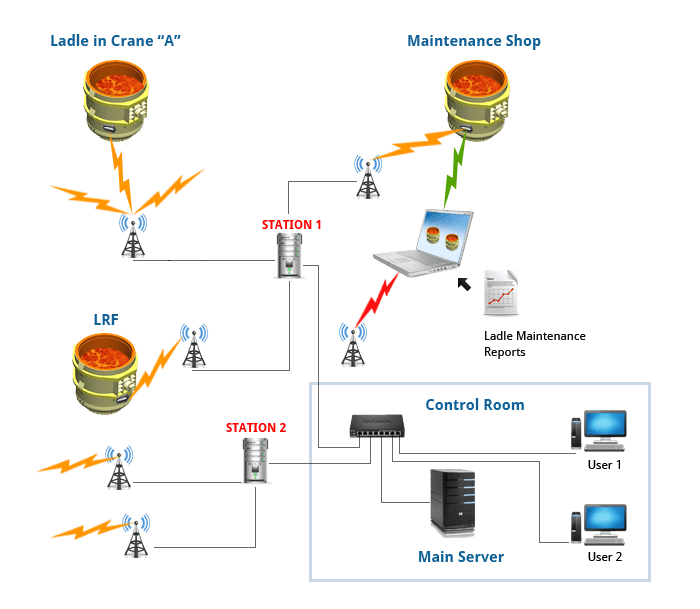
A real-time Ladle Tracking System (LTS) provides complete information about ladle be-it the ladle heat information, exact ladle position, ladle idle time, ladle life, exact contact time with hot steel, causes of delay and maintenance requirement. The system detects exact arrival & departure time for each ladle to the processing area along with it's idle time. From the information supplied by the automation system, the LTS maps the heat information, exact processing time and temperature profile for each ladle.
The LTS captures all the information from the maintenance work performed on a particular ladle and gives a clear understanding of the ladle availability for future heats. The system also maintains past history of the ladle which helps supervisor to analyze ladle profile. Ladle profile includes ladle life, heat-wise history, temperature profile, aging etc.
- Equipments
- Scheme
- Features
- Benefits
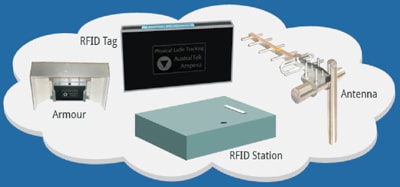
RFID Tag
The RFID tags are passive and use a modified form of the RFID reader's own signal to transmit data. Essentially, the tag reflects the RF signal transmitted by the reader and embeds its unique ID by modulating that reflected signal. The unique identification number will not change during the lifetime of the tag. The tags can be read from several feet away and they don't need to be on the line of sight of the reader. The system detection distance between sensors and antennas is recommended to be limited to 22 meters; however the detection distance has been site-tested up to 30 meters.
RFID Protection Armor
In order to protect the RFID Tag from both high temperature and collisions with other equipment, the RFID tags are installed inside a special protective cover called "armor", which is welded to the ladle wall. The armor location on the ladle depends on ladle wall temperatures and where it will be safe from collisions and from signal interference. The armor keeps the sensors' temperature range within working levels to allow correct data transmission. The armor protects the sensors from collision damage, from hot metal splashes, and from slag falling from top of the ladle. The armor is manufactured in special steel with several layers of insulation on the internal side where the RFID tag is located.
Stations
The RFID readers are installed inside the stations, which are NEMA 12 enclosures that protect the RFID readers from the environment. The stations have forced ventilation to keep the RFID reader within working temperature ranges and all necessary electrical distribution for powering and protecting the equipment. The RFID readers can manage up to 4 different antennas, which are individually connected to the reader with coaxial cable. The high gain, directional antennas are directed to the locations where the ladles need to be detected.
Antenna
The antenna's gain, measured in dBi (decibels relative to isotropic radiator), is selected depending on cable length and the maximum distance between the antenna and the ladle location. Typically 3, 6, 9 and even 12dBi antennas can be used. During system installation, each antenna is carefully installed, oriented and calibrated to cover a defined area of the plant, which we call spots. Typical spots in a melt shop are the tapping area, cranes, LF, ladle cars, caster turret arms, and pre-heaters.
- Travel time and other Ladle/Torpedo movement statistics
- Plant Mimic with Graphical Ladle/Torpedo Movements
- Keep track of relationship between Ladle - Heat - Processes (production information required)
- Keep the status of all supervised objects and their alarms
- Log recording of alternate operations such as ladle maintenance etc.
- Provide information for Reports such as "Idle Times", "Empty Times", "Average Travel Times" etc.
- Totally expandable (Detection stations as per need)
- KPI
- Impact
- Result
- Idle Time
- Decreased
- Increased Ladle Life & Reduced Maintenance
- Availability
- Increased
- Enhanced Scheduling
- Visibility
- Real Time
- Better Decision
- Thermal Profile
- Accurate
- Prediction of Ladle Lining Temperature
